


 U.Mars — Encyclopedia
U.Mars — Encyclopedia
Basic Astronomy and the Nighttime Sky
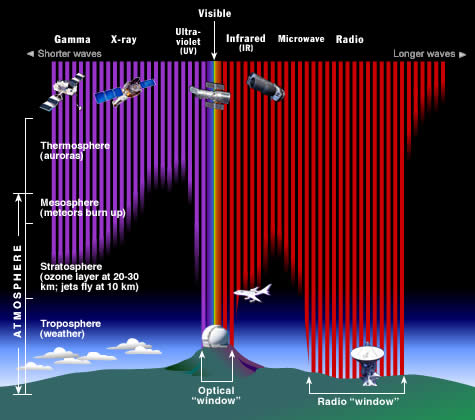 Ground-based telescopes are limited in what wavelength ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum they can see, due to absorption of many forms of light by atmospheres. On Earth, only visible light (plus a small portion of nearby infrared and ultraviolet) and radio waves reach the surface, as in the image on the right.
Ground-based telescopes are limited in what wavelength ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum they can see, due to absorption of many forms of light by atmospheres. On Earth, only visible light (plus a small portion of nearby infrared and ultraviolet) and radio waves reach the surface, as in the image on the right.
Clearly, deep infrared, x-ray, gamma ray, and some other kinds of telescopes could only be placed in space (or on a body without an atmosphere).
In addition to the limitations caused by atmospheric absorption of many forms of light, even visible light rays are slightly deflected by pockets of air of different temperatures. These alternating pockets of warmer or cooler air behave like little lenses, bending the path of light from distant objects and causing a slightly blurred image. An observatory in space does not have this problem, as illustrated, below.
The following animation shows how analysis of many images taken of the same targets from a ground-based telescope can remove atmospheric blurring.

Movie credit: Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy Infrared Interferometry Group
Of course, in addition to wavelength restrictions and atmospheric effects, a ground-based telescope can only watch targets that are currently above their local horizon, at nighttime, when the weather is clear. A space-based telescope can often track a target continuously for several days without interruption.
One might wonder why there are not more space-based observatories — but they are vastly more expensive than ground-based ones, and have certain size limitations brought on by the difficulties in launching large pieces of equipment off the Earth's surface. In addition, many space-based observatories become completely out of reach for any possible service or upgrades that may be desired.
See also:
Thanks to:
Space Telescope Science Institute. (2005). Telescopes from the Ground Up. Retrieved January 12, 2014, from: http://amazing-space.stsci.edu/resources/explorations/groundup/